Alan Turing, a name synonymous with modern computing, was a British mathematician, logician, and cryptanalyst whose groundbreaking work during the mid-20th century laid the foundation for computer science.
Among his many contributions, the most significant is undoubtedly the invention of the Turing Machine, a theoretical construct that remains a cornerstone in the field of computational theory.
Turing Machine: A Revolutionary Concept
In 1936, Turing introduced the concept of the Turing Machine in his seminal paper, “On Computable Numbers, with an Application to the Entscheidungsproblem.”
The Turing Machine is an abstract device that manipulates symbols on a strip of tape according to rules. Despite its simplicity, the machine is powerful enough to model the logic of any computer algorithm, making it a universal computing machine.
The Turing Machine contains several key components:
Tape: An infinite strip divided into cells, each capable of holding a symbol.
Head: A device that reads and writes symbols on the tape and can move left or right one cell at a time.
State Register: Stores the current state of the Turing Machine from a finite set of states.
Table of Rules (Transition Function): Dictates the machine’s actions based on the current state and the symbol it reads on the tape.
The machine begins in an initial state and reads the symbol in the current cell.
Based on the transition function, it writes a new symbol, moves the tape left or right, and transitions to a new state.
This process continues until the machine reaches a halting state, producing an output or solving a problem.
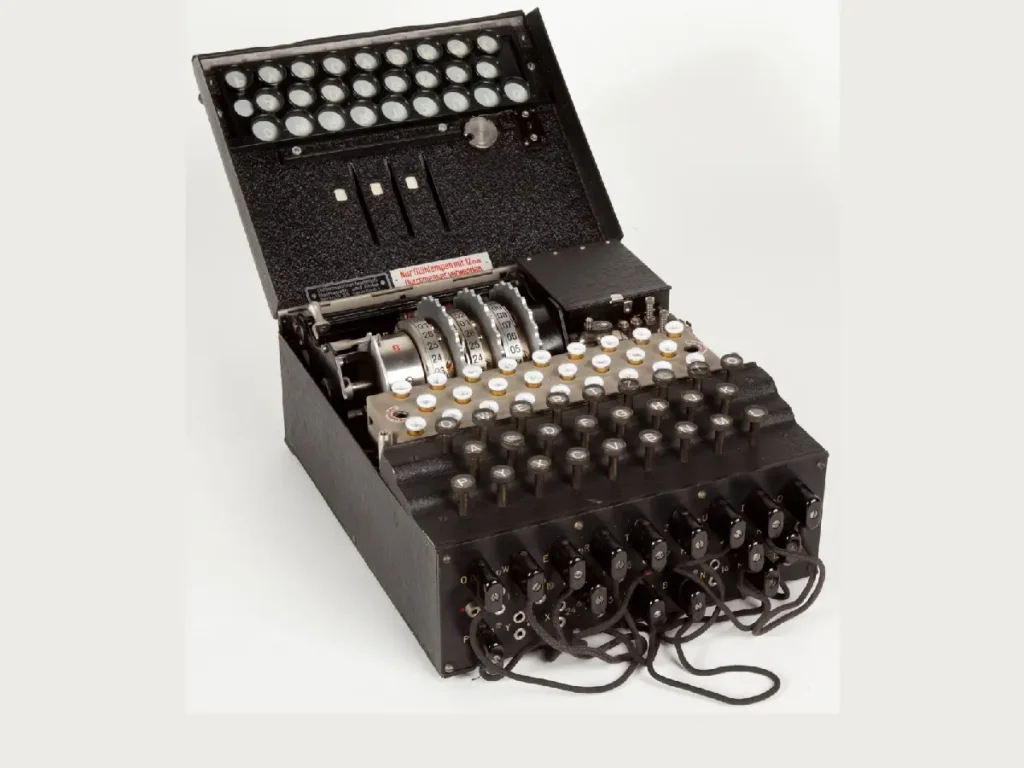

The Impact on Scientific Society
The Turing Machine was not just an abstract idea; it provided a rigorous framework for understanding what it means for a function to be computable.
This theoretical underpinning is vital to the development of computer science as it helps define the limits of what can be computed.
Foundations of Computer Science: Turing’s work formalised the concept of algorithms and computation, leading directly to the development of modern computers.
The Turing Machine serves as a fundamental model in computer science curricula worldwide.
Artificial Intelligence: Turing’s later work, including the famous Turing Test, explored the potential for machines to exhibit intelligent behaviour. This was the seed that grew into the field of artificial intelligence.
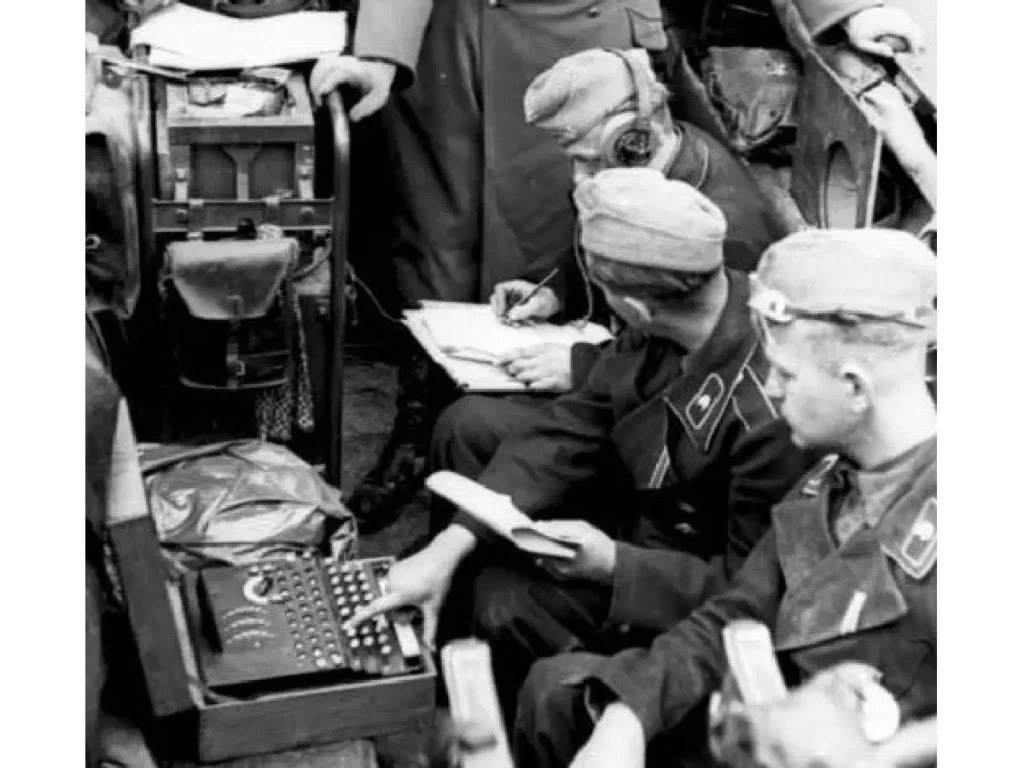
Cryptography: During World War II, Turing’s expertise was crucial in breaking the German Enigma code, significantly contributing to the Allied victory. His work in this area laid the groundwork for modern cryptographic practices.

Lesser-Known Aspects of Turing’s Life
While Turing’s professional achievements are widely celebrated, several fascinating and lesser-known aspects of his life also deserve attention.
Early Genius: Turing’s brilliance was evident from a young age. He taught himself to read in three weeks and showed an early fascination with numbers and patterns.
The Turing Test: Proposed in his 1950 paper “Computing Machinery and Intelligence,” the Turing Test was designed to determine whether a machine could exhibit human-like intelligence. This concept remains a critical benchmark in AI research.
Tragic End: Despite his monumental contributions, Turing’s life ended tragically. In 1952, he was prosecuted for homosexual acts, which were then illegal in the UK.
Subjected to chemical castration, Turing’s life took a downward spiral, leading to his untimely death in 1954, ruled as suicide by cyanide poisoning. However, some speculate it might have been accidental.

Alan Turing’s legacy is one of intellectual brilliance and profound impact. The Turing Machine remains a vital theoretical tool in understanding computation, while Turing’s broader work laid the groundwork for numerous fields, from computer science to artificial intelligence.
Recognizing both his achievements and the injustices he faced provides a fuller picture of a man who changed the world but was tragically mistreated by it.
As we continue to explore the realms of technology and artificial intelligence, Turing’s pioneering spirit and intellectual rigour serve as enduring inspirations.
His contributions remind us that the quest for knowledge and understanding is a journey that can transform society in unimaginable ways.



